In December 2024, Hyundai Rotem was nominated for the signal system project for the Daejang-Hongdae Line railroad by Western Metro. The Daejang-Hongdae Line is a metropolitan railway that runs approximately 20 kilometers between Daejang-dong, Bucheon-gu, Gyeonggi-do, and Hongdae Station, Seoul. Hyundai Rotem will supply the Korea Train Control System-Metro (KTCS-M), which is necessary for the stable unmanned operation of the line. KTCS-M, a next-generation railway signaling system developed by Hyundai Rotem in 2014 as part of a government project, is a signaling system that can track the vehicle’s location in real-time by utilizing 4G railway wireless communication, LTE-R. The Daejang-Hongdae Line signaling system project is notable as it will introduce Hyundai Rotem’s advanced, localized train signaling system.
In addition, Hyundai Rotem recently enhanced the competitiveness of its signaling system by successfully developing an EIE(Electronic Interlocking Equipment) and ATS(Automatic Train Supervision), which are integral components of the wayside signaling system. These advancements ensure an organic connection between track circuits and signals, ensuring the safe operation of trains and facilitating the full-scale commercialization of KTCS-M. The EIE has received recognition for their safety and reliability by achieving the highest Safety Integrity Level (SIL) 4 from an Independent Safety Assessor (ISA), while the ATS achieved SIL 2.
This article highlights the evolution of Korean train signaling systems, led by Hyundai Rotem, and underscores the significance of its recently developed EIE and ATS.
What is a Railway Signaling System?

Trains travel at high speeds. In other words, it requires precise guidance through signaling mechanisms and a high level of safety as it carries numerous passengers daily. The control system that facilitates the accurate and secure operation of trains is referred to as a “signaling system.”
Railway signaling systems are installed both within the train (onboard) and at Automatic Train Supervision (ATS) to ensure the safe operation of trains through real-time networking among various systems. Furthermore, precise construction and operation are required as key elements such as wayside signals, traffic lights, track switches, railroad crossings, track circuits, and safety facilities work together seamlessly.
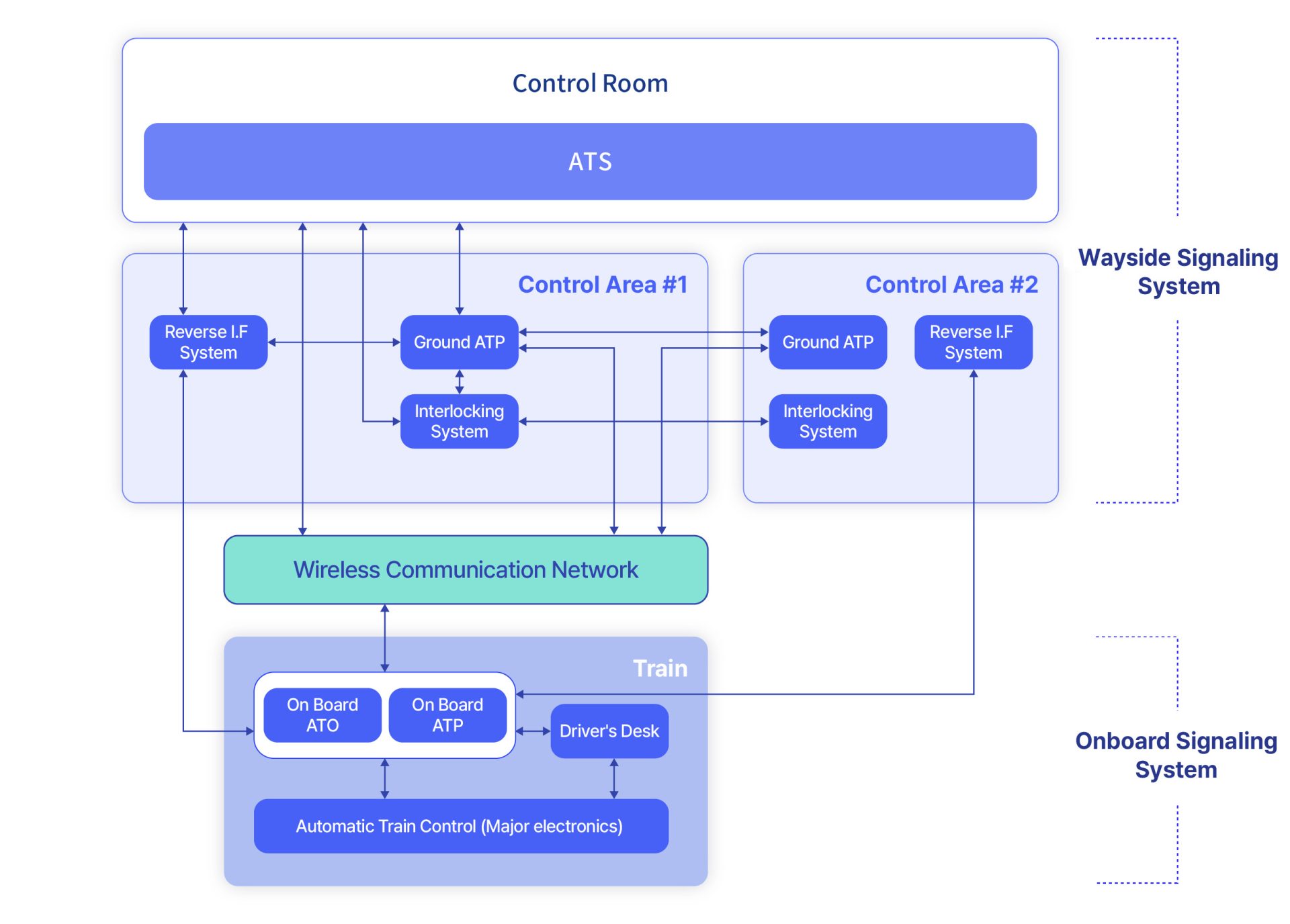
Railway signaling systems can be broadly categorized into two types: “Onboard Signaling System” and “Wayside Signaling System.” The onboard signaling system is located within the rail vehicle and is predicated on the train protection function (ATP), which prevents collisions by calculating the train’s position in real time. This system facilitates the operation of trains through signal commands that ensure safe gaps between trains, interlocking of tracks, and adherence to speed limits. Recently, automatic or unmanned operation capabilities (ATO) have been integrated to enhance operational efficiency.
Wayside signaling systems comprise a much more diverse range of equipment and complex structures. The typical components of the wayside signaling system are the Electronic Interlocking System (EIE), which controls the train’s course by connecting with trackside facilities on the ground such as signals, track switches, and track circuits; the Wayside Signaling System (WATC, RBC, etc.), which controls the speed of the train by providing the appropriate speed to the vehicle based on the position of the track; and the Automatic Train Supervision (ATS), which monitors and controls all trains and equipment by exchanging train operation information with the EIE and ATS.
Hyundai Rotem’s Journey to Strengthen Railway Safety with SIL 4 Certification
Given the life-or-death stakes associated with railway signaling, where even a minor malfunction could lead to devastating accidents like train collisions or derailments, it’s crucial to undergo rigorous safety verification from an ISA. A key standard for ensuring signaling system safety is the “Safety Integrity Level (SIL)” certification. This certification is awarded by an ISA in accordance with European Norm (EN) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standards.
SIL certification evaluates the reliability and safety of equipment across various industries, including railways, nuclear power, and medical devices. The certification is divided into four tiers (SIL 1 to SIL 4): SIL 1 represents the lowest level of safety integrity, where the probability of failure is once in 1 to 100 years. SIL 2 means once in 100 to 1,000 years, and SIL 3 means once in 1,000 to 10,000 years. SIL 4 represents the highest level of reliability, meaning the probability of failure is as low as once in 10,000 to 100,000 years. The higher the SIL level, the lower the risk of system failure.

In South Korea, the Railway Safety Act was revised in 2018 to mandate SIL 4 certification for railway signaling systems. Furthermore, most international railway projects now require SIL 4 certification, making it an essential criterion for any newly developed signaling systems.
Starting with the CBTC wireless communication-based train control and signaling system for the Almaty Metro in Kazakhstan in 2014, Hyundai Rotem has obtained SIL 4 certification for multiple onboard signaling systems, such as KRTCS (now KTCS-M), ETCS-L2 (now KTCS-2), the ATP/ATO system for Cairo Line 2, and the Balise Transmission Module (BTM), a core component of KTCS.
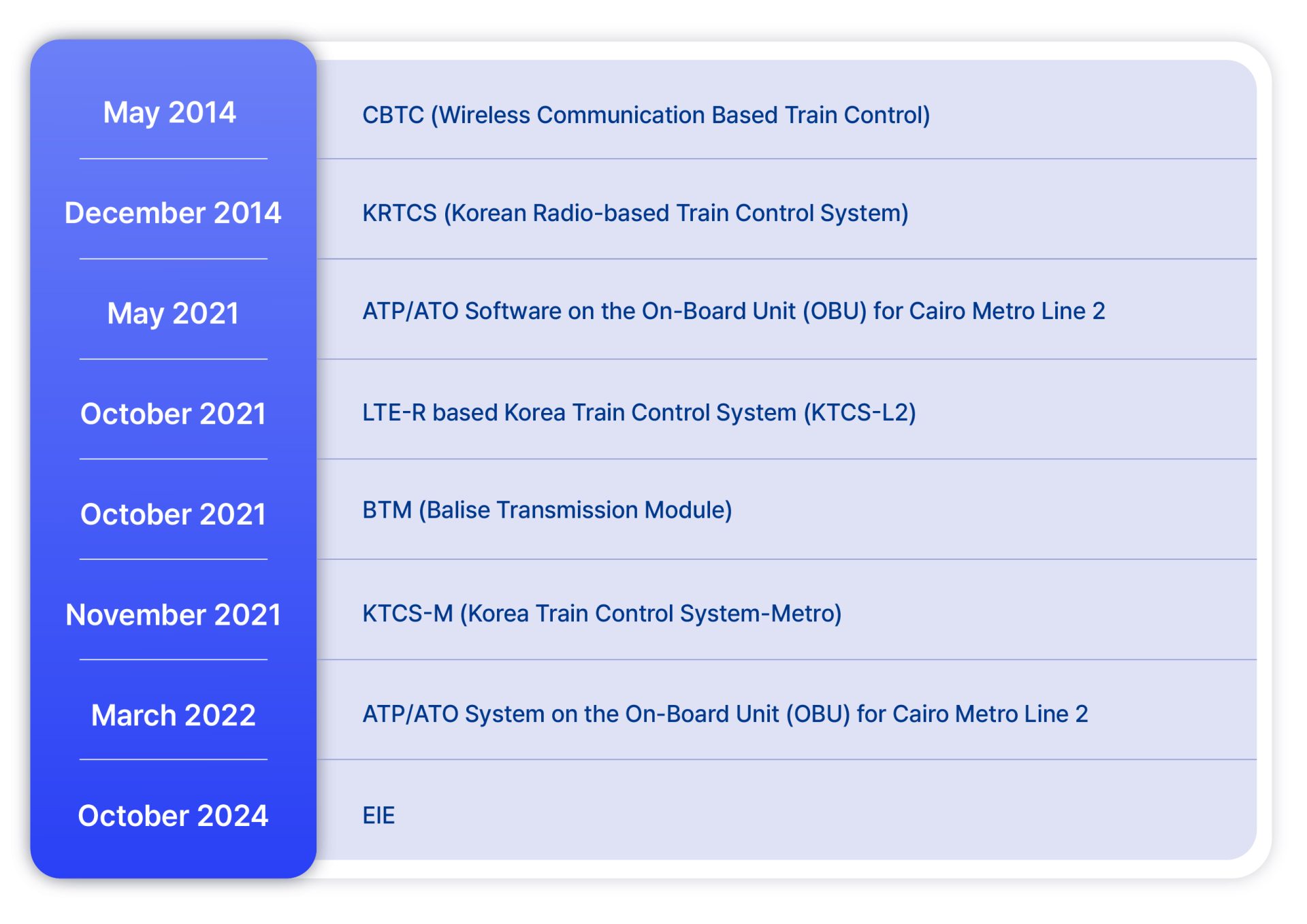
Achieving SIL 4 Certification and Type Approval in a Short Time through In-House Technology Development
In October 2024, 33 months after initiating the in-house development of EIE in February 2022, Hyundai Rotem achieved a major milestone by obtaining the SIL 4 certification from an ISA. Additionally, the company became the first to receive a type approval certificate for railway products from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport. Typically, the type approval process takes over a year. Still, by closely coordinating with the Korea Railroad Research Institute from the planning stage and proactively addressing inspection agency requirements, Hyundai Rotem successfully reduced the certification period to just six months.



Streamlined certification processes by collaborating with KRRI
Hyundai Rotem’s latest EIE is designed to meet the SIL 4 safety standard and comply with the Korean Railway Standards (KRS SG 0015-20). Beyond meeting these regulatory requirements, EIE also enhances interlocking system control capabilities, a key function in railway signaling systems. While securing stable and high-performance control, Hyundai Rotem applied high-spec H/W to offer centralized and decentralized configurations. This advancement consequently allows to expand the range of options available to customers.
* Centralized EIE: an interlocking logic rack is installed at each station
* Decentralized EIE: interlocking logic racks are centralized in a single location (typically the signaling room at the depot), with only the input/output modules installed at each station.
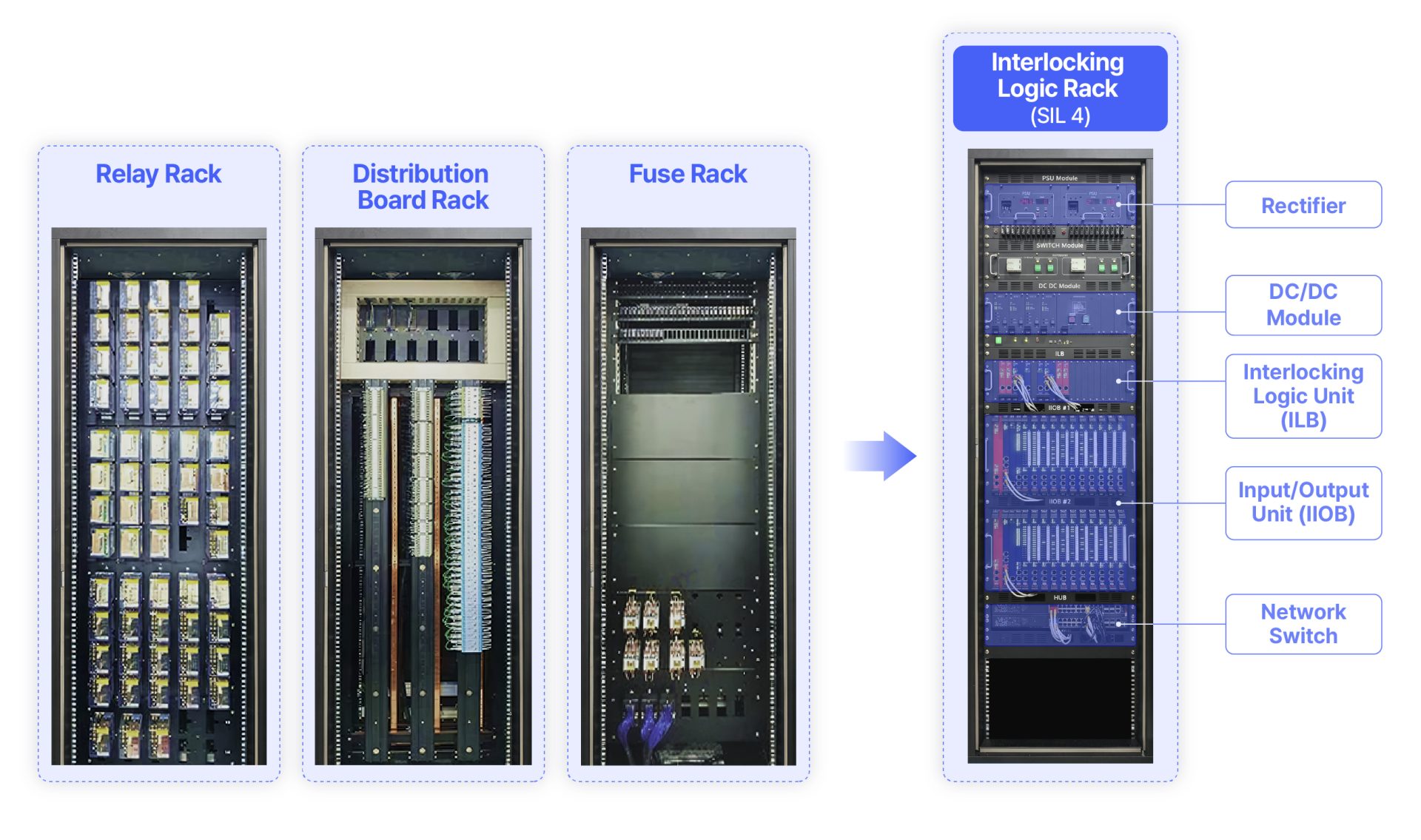
Hyundai Rotem has also tackled a major industry hurdle by internalizing the core technologies. Railway signaling systems that rely on external components often deal with lengthy troubleshooting processes and compatibility concerns. However, by developing in-house EIE, Hyundai Rotem has successfully overcome such interoperability issues.
The company began to develop ATS together with EIE in 2022 and proudly achieved their SIL 2 certification from an ISA in December 2023. The most standout feature of this new ATS is its modular architecture, allowing smooth integration across various railway networks, including trams, metros, and mainlines. The development of the ATS has enabled unmanned operations across diverse routes and rolling stock. Given that ATS need to meet specific operator requirements, this innovation is set to greatly enhance customization, improve maintenance efficiency, and support long-term system management.
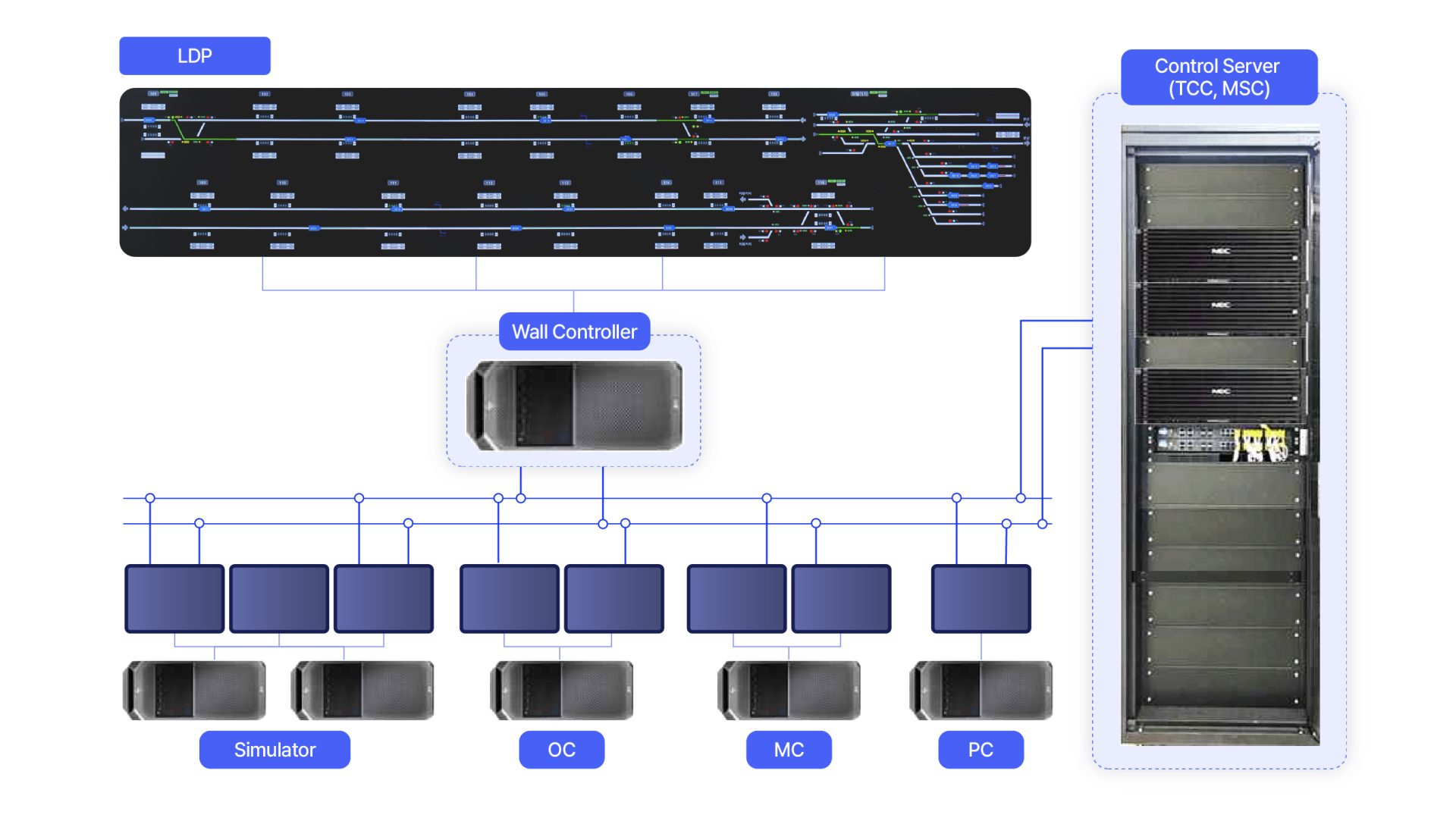
*TCC(Train Control Computer): The central server of the ATS
*MSC(Management Support Computer) ATS schedule management server
*LDP(Large Display Panel) A comprehensive display panel that provides real-time operational information
*OC(Operator Console) A control interface for monitoring and managing on-site facilities, train status, and schedules
*MC(Maintenance Console) A maintenance support system that tracks alarms, events, and system diagnostics to ensure smooth operations
*PC(Programmer Console) A tool for creating and reviewing offline schedules, verifying schedule requests, and analyzing performance data
In a bid to further enhance the independent development of core wayside signaling system infrastructure, Hyundai Rotem has constructed an “Integrated Signaling Test Room” at its test building of the Rail Solution R&D Center and established the integrated test process to implement an integrated interface between devices and reduce the chances of failures in the field. The Test Room is equipped with a range of facilities, including EIE, ATS, RBC, and simulators. These resources allow for thorough testing of system integration and functionality. Engineers can validate the physical and logical interfaces between actual devices before any installation on the main line, thereby preventing potential failures that could arise in the field by testing past rolling stock and various scenarios in this room. The room also facilitates the pre-validation of functions under unmanned driving conditions. This extensive pre-deployment verification not only enhances the quality and reliability of Hyundai Rotem’s signaling systems but also significantly reduces rework costs.
Implications of Hyundai Rotem’s In-house Development of Wayside Signaling Systems
Hyundai Rotem’s successful development of EIE and ATS represents a significant milestone that goes beyond merely localizing essential Wayside signaling technologies. Specifically, the EIEs used in the KTCS-M signaling system—engineered for urban and light rail transits—facilitate fully autonomous train operations, which require much more sophisticated technology surpassing traditional railway signaling systems. This innovation has bolstered Hyundai Rotem’s global competitiveness in railway signaling systems, as these EIEs can be seamlessly adapted across various railway networks, including metro, intercity, tram, and high-speed railways.
Moreover, with the Type Approval Certification from the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport and the SIL 4 certification, Hyundai Rotem is now well-positioned to capitalize on more business opportunities. The type approval enables the company to participate in any Wayside signaling projects in Korea. At the same time, the SIL 4 certification reinforces its standing in the international railway market, demonstrating compliance with the latest European EN standards required for global projects.
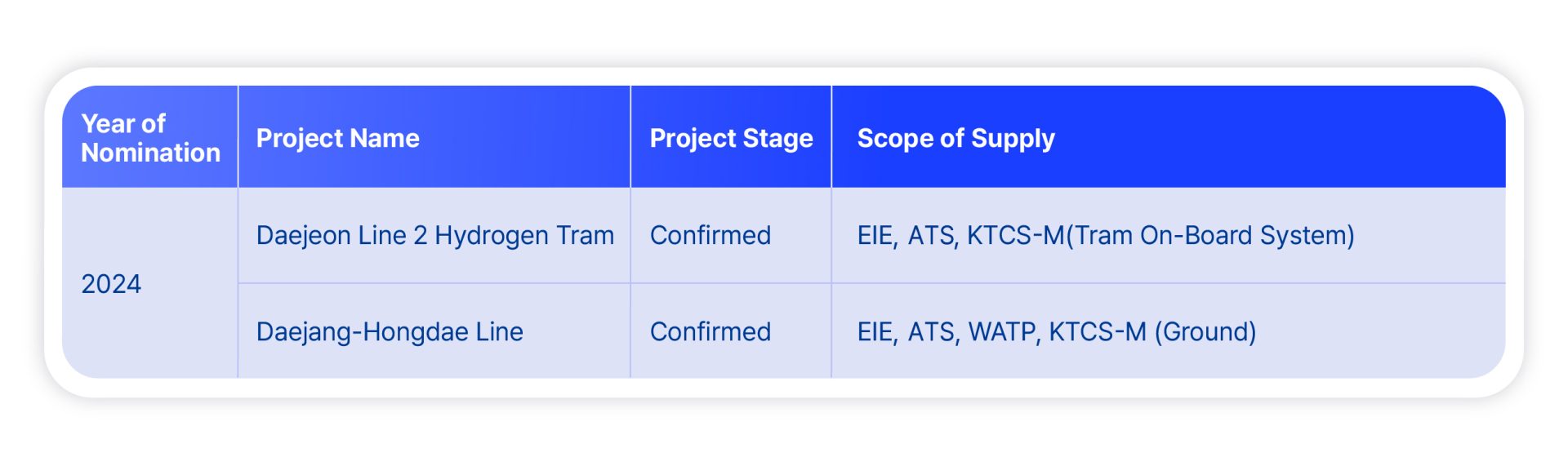

Hyundai Rotem has been at the forefront of developing railway signaling systems in South Korea, catering to a diverse range of transportation options, including high-speed trains, electric trains, and trams. As signaling systems equipped with Hyundai Rotem’s technologies have steadily entered operation, the number of routes utilizing these innovations continues to grow. By internalizing key technologies related to wayside signaling systems, Hyundai Rotem has positioned itself as a specialist in total railway signaling solutions, encompassing on-board signals, wayside signals, EIE, and ATS.
As global railway leaders increasingly seek to place orders for both vehicles and signaling systems, Rotem’s new total signaling system solution can create synergy with its existing vehicle lineup. That is the reason Rotem is expected to be highly competitive in the market. Looking ahead, the company plans to strengthen its operational performance by enhancing customer service (CS) and quality control in the field, building on its experience and expertise, and ultimately accelerating K-Rail’s global expansion.



