
Some of the most appealing contents to corporations as of late are virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). There are many VR and AR technology developments and content productions centered around the field of culture and art including games, performances and exhibitions and the sales of relevant industries continue to grow at a rapid pace every year.
Virtual Convergence Technology Expanding into Manufacturing Business
Virtual convergence technology is not only receiving the spotlight in the entertainment industry. According to the ‘2021 VR/AR Industry Survey’ published by the Ministry of Science and ICT, it was revealed that the number of companies producing industrial contents (251 companies) among companies in the VR and AR industry in Korea was the highest following the number of companies producing cultural contents. Also, digital twin, a technology expected to become the ‘game changer’ in the future, is a technology based on virtual convergence technology and many companies are investing in the development of related technology.
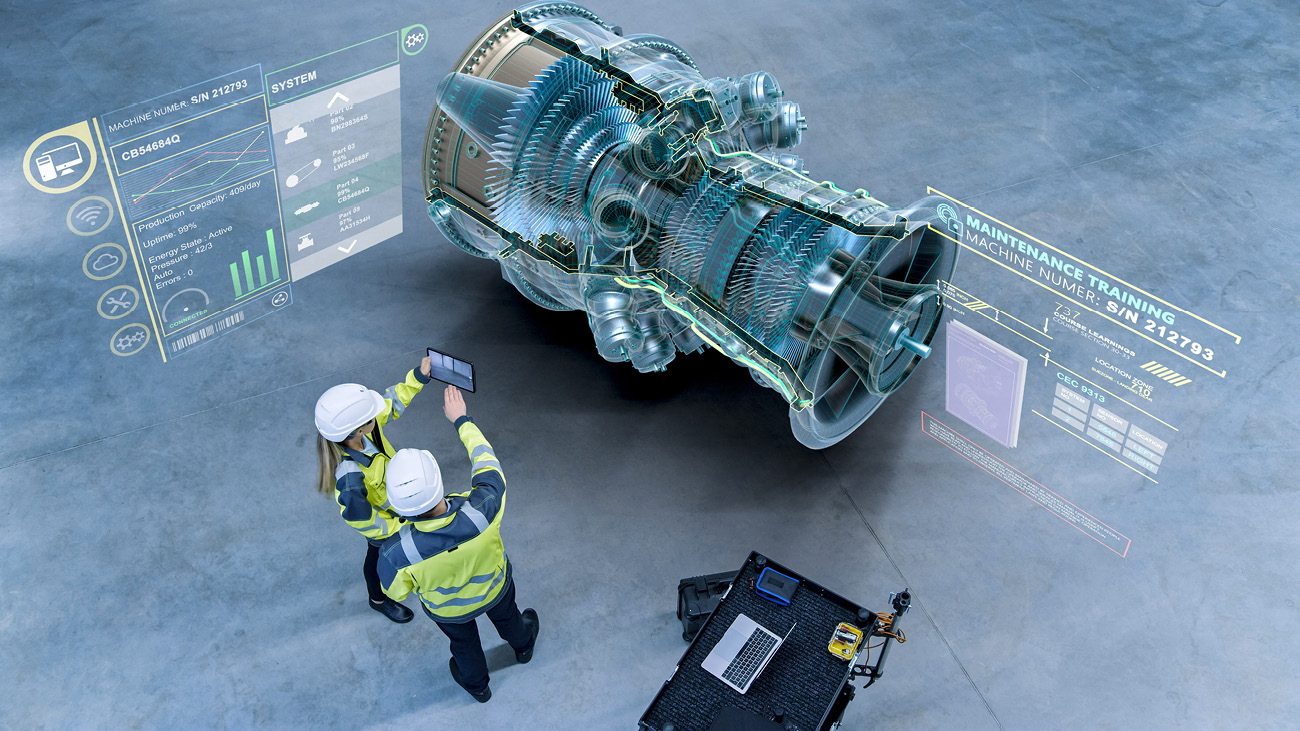
Relevant industries are envisioning the final form of virtual convergence technology as the materialization of the ‘metaverse’. To achieve this vision, companies are aiming to pre-emptively develop mixed reality (MR) and eXtended reality (XR), which are evolved forms of VR and AR and to apply them in the manufacturing industry. If such advanced virtual convergence technology is actually applied, then digital twin can become a reality through a ‘virtual factory’ in a perfectly built virtual world.
Companies in the manufacturing industry are focusing on the fact that virtual convergence technology can offer efficient utilization of ‘remote support.’ There are machine designs and maintenance-related technologies utilizing VR and AR technology being developed with the goal of materializing technology that allows multiple participants to communicate and interact from unspecified locations through a single content.

Virtual convergence technology is especially projected to be of high utility in maintenance of railway vehicles. Traditional railway vehicle maintenance required actual vehicles and parts for normal training and exercises. But with utilization of VR/AR contents, training can be administered across various fields regardless of time or location. Subsequently, Hyundai Rotem has established the ‘VR & Data Analysis Lab’ and is developing training contents utilizing AR and VR technology. Currently, the lab has completed developing part assembly/disassembly and a vehicle operating manual contents and is in the process of verifying the validity of the contents.
Maintenance Training Contents Utilizing Augmented Reality from Hyundai Rotem
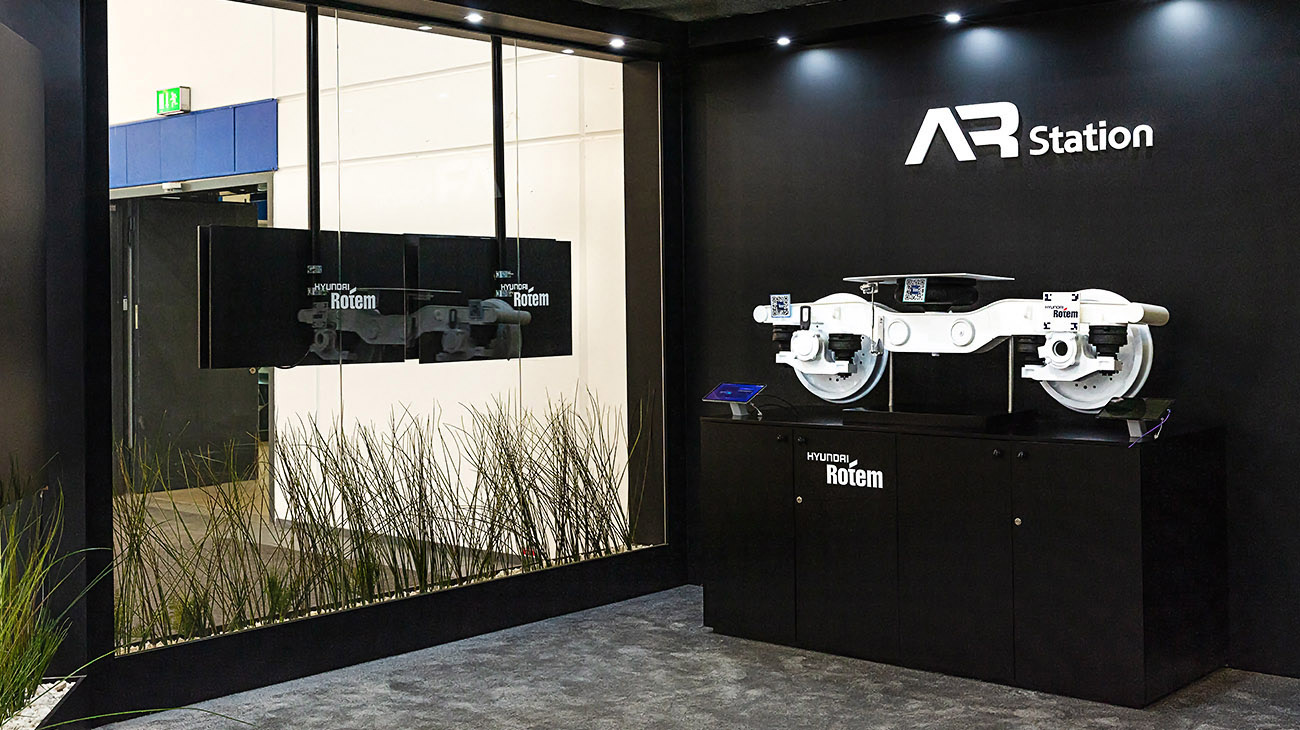
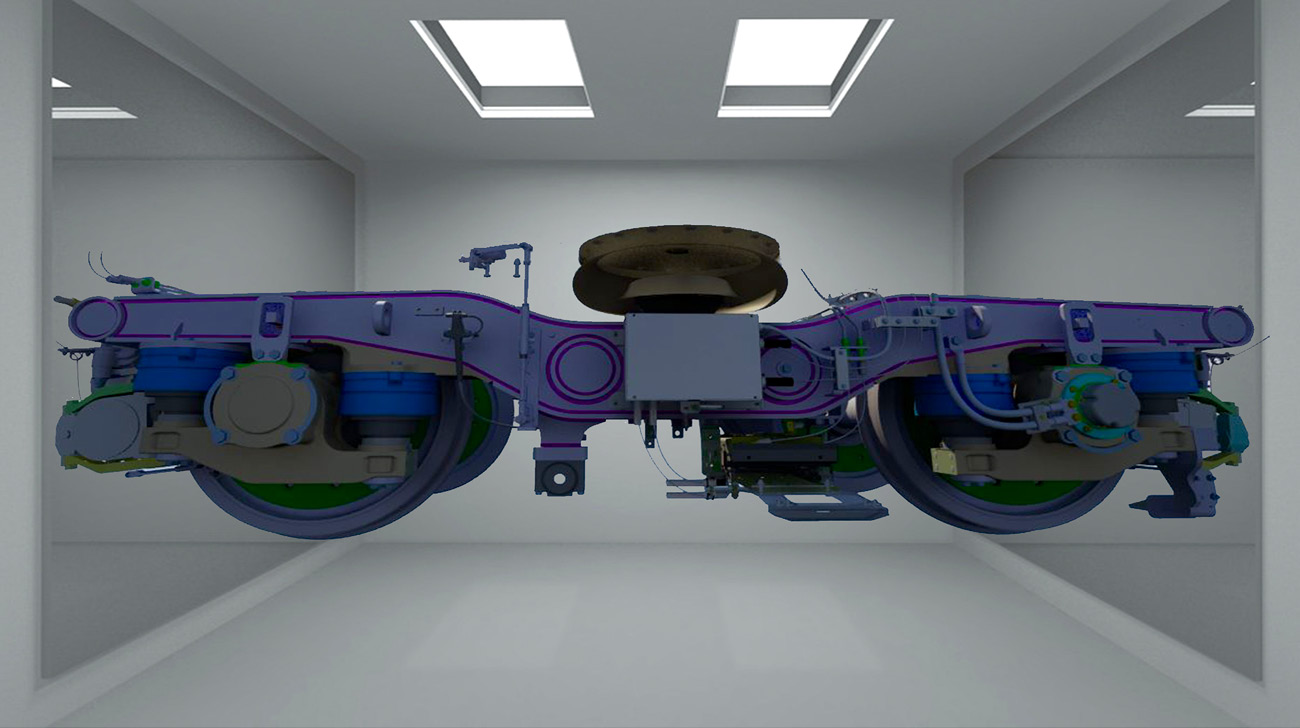


Hyundai Rotem has developed contents integrating AR technology for railway vehicle maintenance training last year. This content can inspect over ten parts including journal box, speed detector and spring and it was designed to have even better training effect by displaying information such as record of inspection and inspection cycle for each part. Scanning the QR code of the vehicle model part with a camera will open the applicable 3D model for the actual parts and the instructor can freely look at the 3D model displayed on the tablet PC.
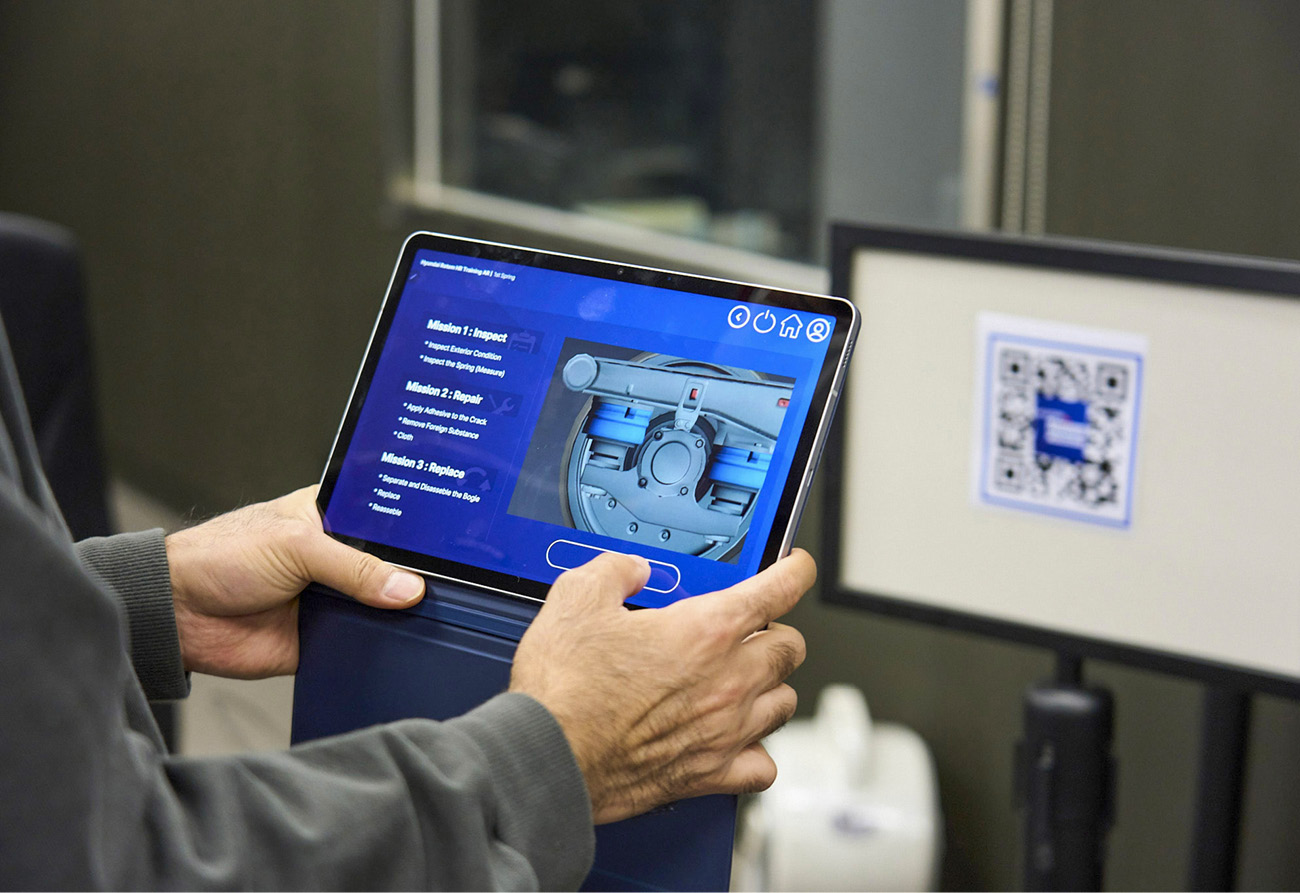

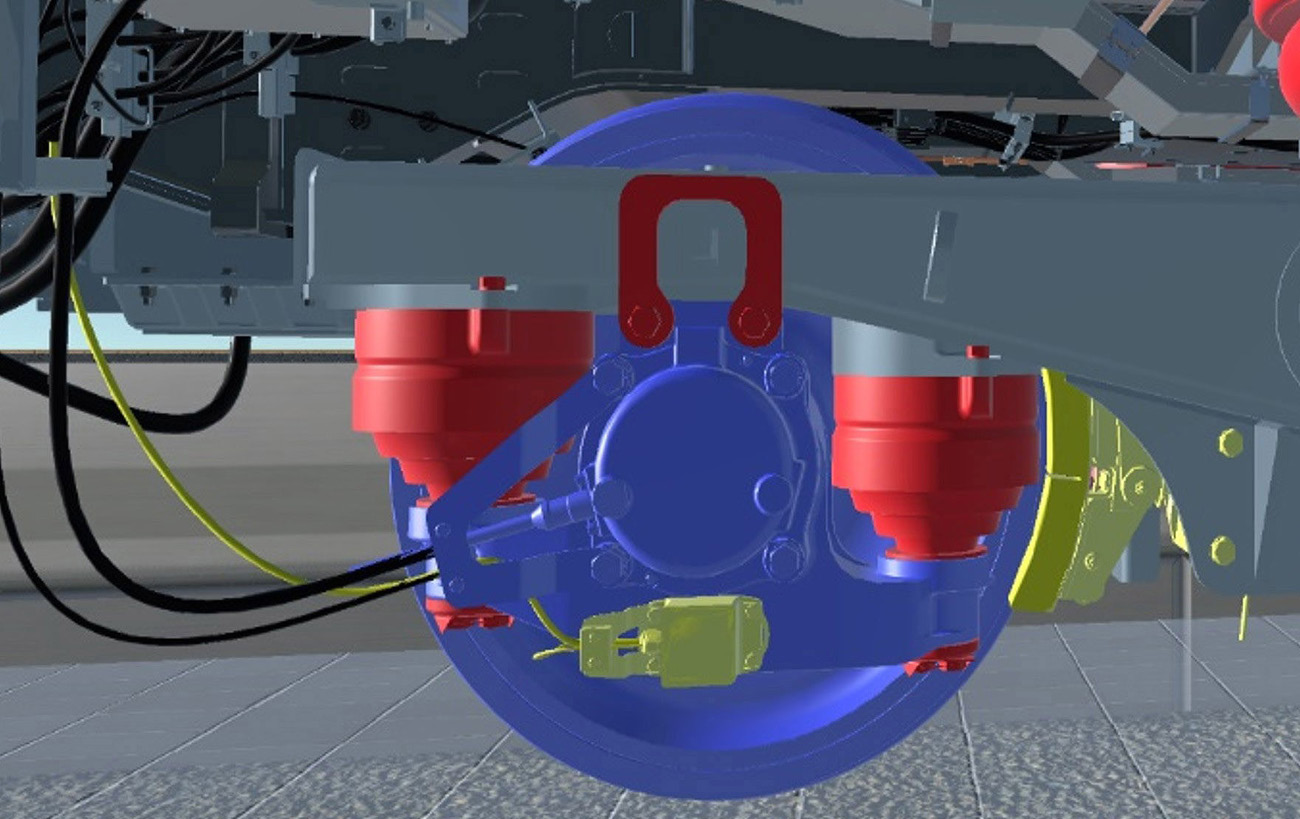
For example, for the first inspection of springs among many vehicle parts inspections, the learner will undergo three phases of learning. The first phase is the ‘inspection’ process, where the learner checks the exterior state of the spring and measures dimensions of the spring for inspection. The second phase is the process of performing appropriate repairs for fractured springs. For example, this would be gluing the fractured portion of the spring with dedicated glue and using a piece of cloth to remove foreign matter. The last phase consists of determining if parts replacement is necessary depending on the size of the fracture and then replacing the parts, if necessary, and reassembling the part to teach learners how to take appropriate measures for applicable issues of each part.
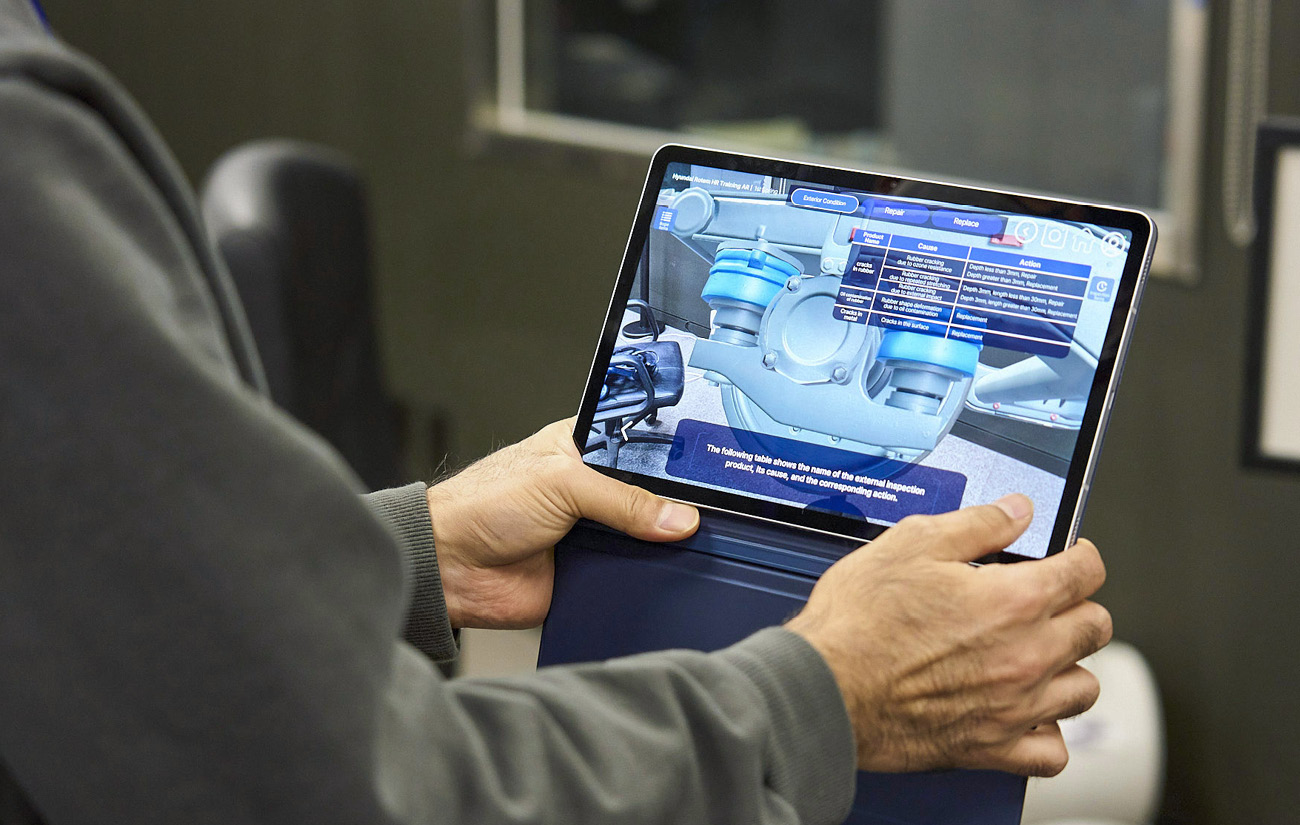

All learning contents feature motion-based interaction for improved realistic feel to provide an experience similar to the process of repairing the actual parts. For example, the content was programmed to recognize motion where the learner drags the cloth up and down for the process of removing foreign matter. The process of applying glue on the fractured area of the part is also performed in a similar manner. Also, as a content for training purposes, all processes feature voice narration for the learner to be able to take accurate measures depending on the situation.
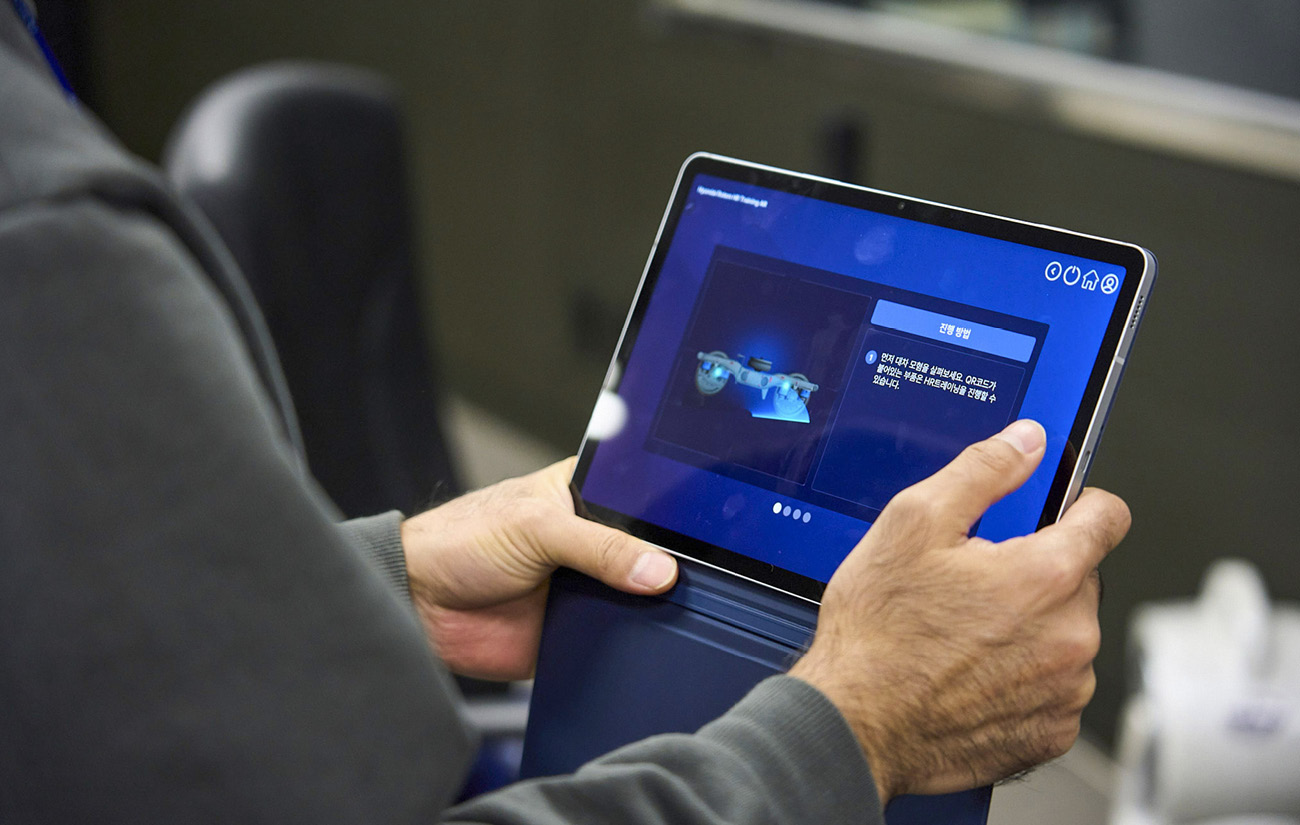

Traditional maintenance-related training consisted of listening to offline lectures from a lecturer or observing and practicing actual maintenance work in the field. On the other hand, AR-based digital contents require only relevant equipment such as a tablet PC and allows quick and accurate training for the theme of the lecture thus establishing itself as an efficient training content. Hyundai Rotem will continue to improve completeness of interaction and system accessibility to improve realistic feel for the learners in the future.
Training Contents Offering Realistic Experience Through Virtual Reality from Hyundai Rotem
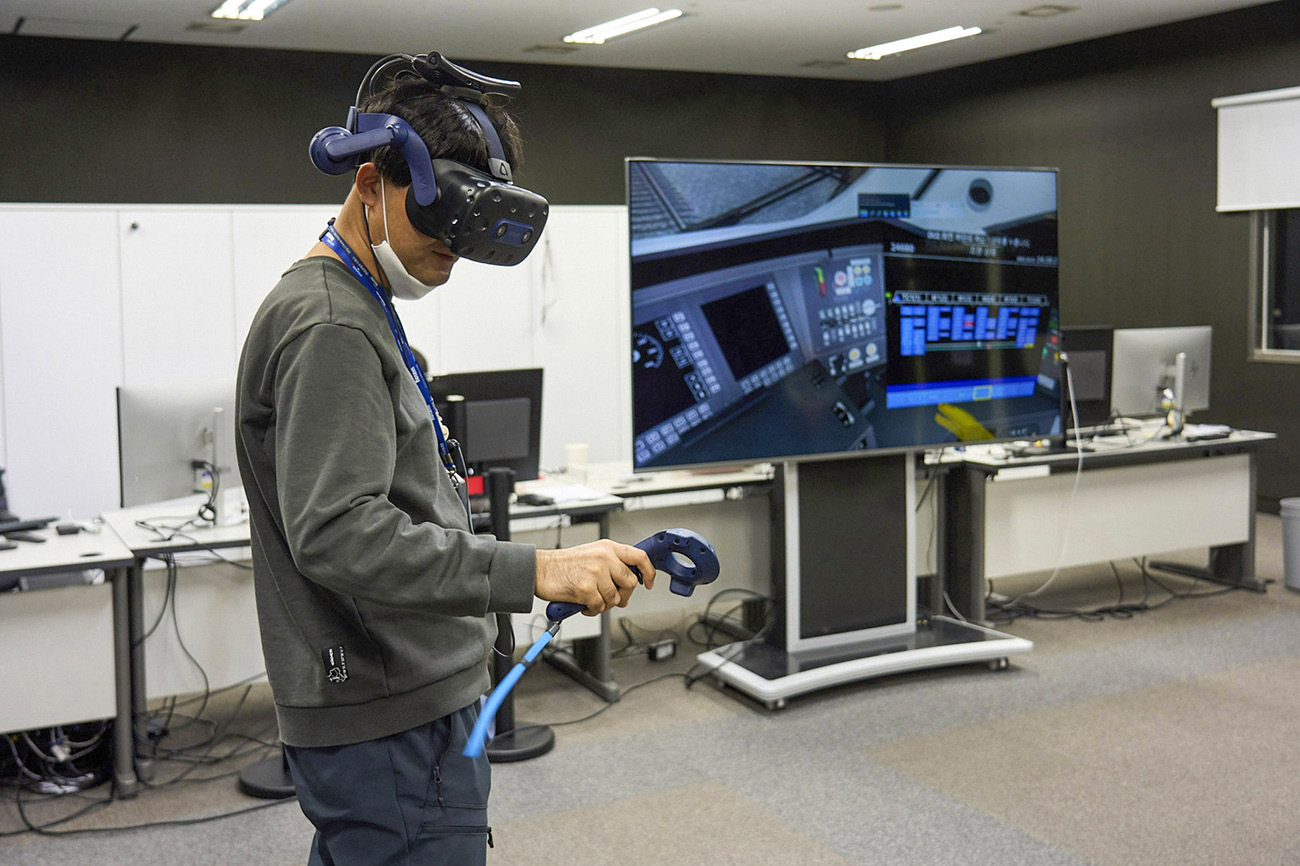

Furthermore, Hyundai Rotem is also close to finishing the development of engineer training contents utilizing VR technology. This content consists of the learner in need of learning the engineer role to wear VR devices and experience vehicle inspection and driving the vehicle. The content begins with the learner boarding the vehicle from the outside and includes various interactions such as the learner opening the vehicle door and operating various buttons via the controller on the VR device.
Once inspection and setup of all configuration panels inside the engine room for vehicle operation are complete, the learner can use the master controller to actually drive a certain distance and use the braking device. In this instance, the software does not allow the vehicle to be driven without the learner properly setting up the dead man’s switch, which adds a realistic feel to the content.

Hyundai Rotem has also considered the nature of VR devices to add convenience to the operating system. For example, the engine room of a railway vehicle features complex and various buttons like a cockpit in an airplane and it is rather difficult to effectively operate all buttons through a VR controller. In order to solve such issue of button operations, the content was designed to be able to zoom in on the areas with buttons through simple interaction to allow more delicate operations of such buttons. The content was also designed to be able to move to a desired space through just operating the controller for learners to conveniently experiencing the content when the VR content is being utilized in a smaller space.
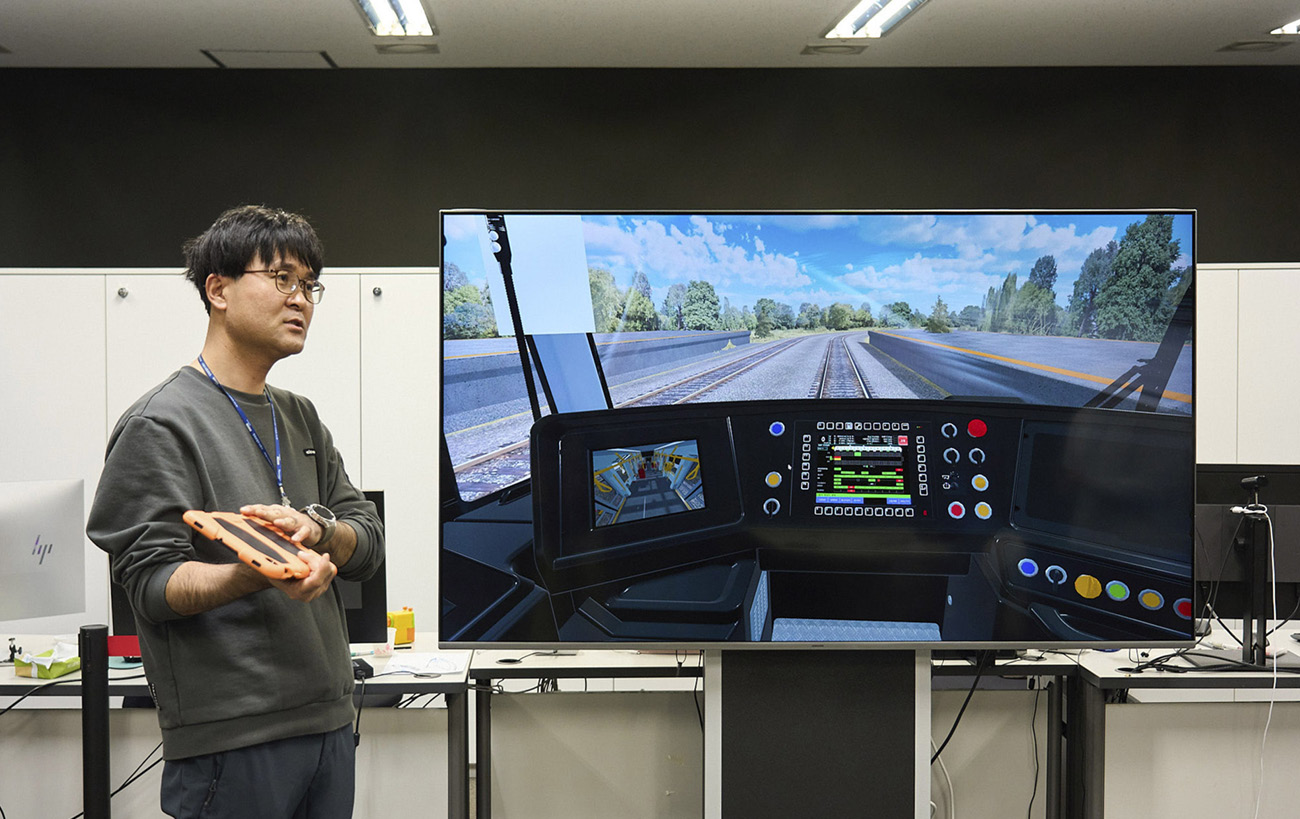

Also, unlike AR contents, narration is provided via text instead of voice to allow the learner to focus on the interaction play as much as possible. Since the VR content is supposed to recreate the actual vehicle in virtual reality, and it focused on the learner being able to easily learn the actual location and operating method of certain controls as the engineer virtually experiences the interior of a railway vehicle.

Currently, 3D modeling of vehicles used in VR and AR contents are based on CATIA data of actual vehicles. With consistency of location, size, etc. of the parts between the 3D model and actual vehicle, CATIA data allow programmers to create an even more realistic interaction when it comes to opening doors or operating parts. However, there are certain areas where the developer edits the data to resolve convenience issues due to the nature of VR technology when the learner is playing the content. Such editing is performed without distorting the properties of the actual vehicle and the team that designed the actual vehicle determines appropriateness of such data editing through VR design verification. At the same time, the VR team delivers feedback to the design team if there is any error discovered during analysis of data for programming interactions and then the design team undergoes the process of supplementing and improving on such errors.

Hyundai Rotem has previously showcased the prototype of the content by operating VR and AR booths for visitors of ‘InnoTrans 2022 Exhibition’ at Berlin, Germany held in September 2022 following its showcase in ‘RailLog Korea’ in 2021. The audience members had the opportunity to directly experience VR contents for engineer training along with the AR contents for maintenance training. At the time, Hyundai Rotem was the only company that has successfully recreated the functions of an actual engine room along with the master controller among railway vehicle content demonstrating companies.

Hyundai Rotem is expected to achieve higher competitiveness compared to other companies while also being capable of having systemic response to emergencies that occur in maintenance through its R&D and prompt application of virtual convergence technology. The company also expects to finish development of the final version of the contents by early 2023 and utilize them for actual training in the future and plans to consistently expand the application of virtual convergence technology for safer and more efficient maintenance and training related to railway vehicles in the future.

