
In trains, which typically have a lifespan of 30 years, operation and maintenance costs account for a significant proportion of the total cost, in addition to the initial outlay for their introduction. Thus, in the train industry, it is crucial to estimate and effectively control these costs. Here we present the Hyundai Rotem LCC Analysis Program (LAP) that is designed to systematically calculate and oversee the comprehensive maintenance costs that may accrue over the life cycle of a train.
Life cycle cost(LCC), the cornerstone of a comprehensive train cost management system

The LCC of a train includes the investment costs for the train’s introduction such as design, manufacturing and testing, and the train’s maintenance and operation costs over a lifespan of about 30 years, and the train’s disposal costs.
In particular, the maintenance costs of a train account for about 30% of the overall LCC. Therefore, it is essential to accurately estimate the maintenance costs in advance and effectively manage them through appropriate controls. For that reason, train operators who introduce, operate and maintain trains, seek from train manufacturers before introducing trains the analysis and estimation of maintenance costs that will incur throughout the life cycle of trains. In the past, they only considered the initial costs for purchase, but now they also consider maintenance costs in decision makings for train introduction. Consequently, the concept of LCC is of great importance in the train purchase business in terms of wise investment decisions, effective cost management, and sustainable operation.
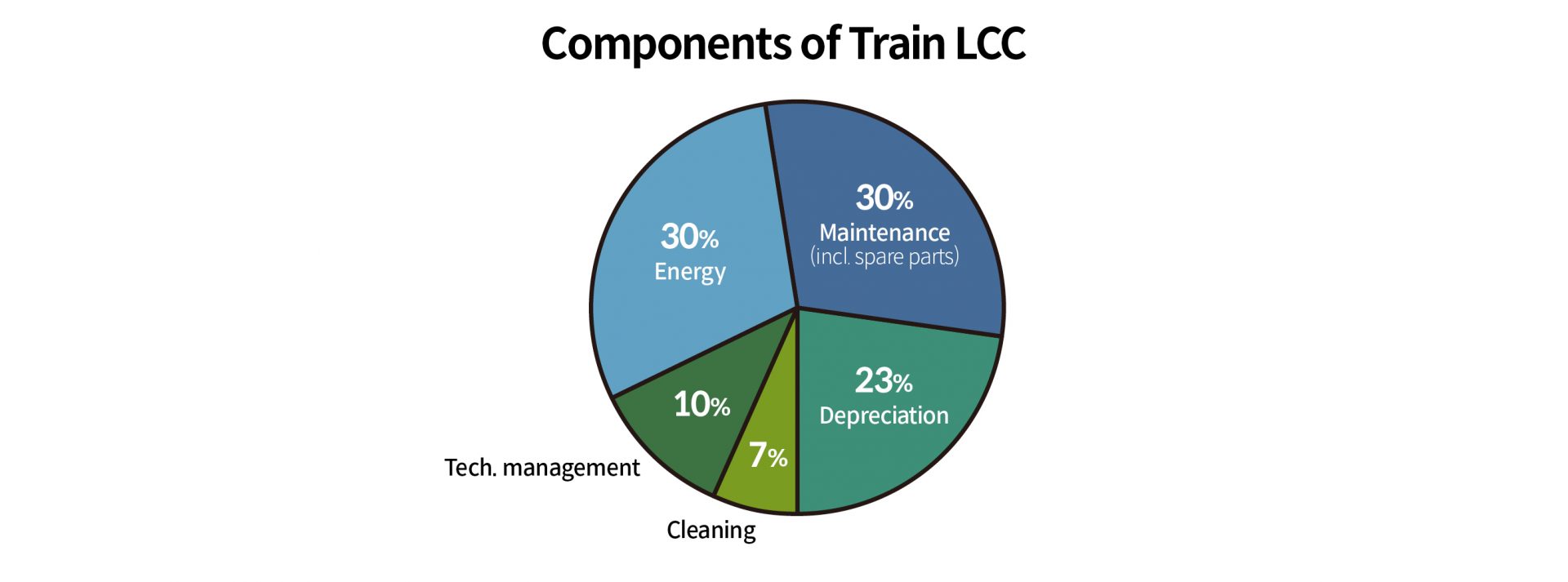
In addition, there is growing trend of entrusting maintenance activities when purchasing trains. This form of purchase has been quite common in the train purchase industry in Europe. In South Korea, the train maintenance sector is also expanding, amplifying the significance of accurate LCC calculation and estimation.
Hyundai Rotem’s train LCC analysis program, LAP(LCC Analysis Program)
In general, train requirements differ among purchasers, and manufacture and maintenance costs vary by design. Calculating these costs is intricate, complex, and time-consuming. Nevertheless, purchasers demand highly accurate and consistent LCC estimates for trains in search before making purchase decisions.
To address this, Hyundai Rotem’s LAP is designed to provide more accurate LCC estimates by compiling essential data required for train LCC calculations. It can shorten the LCC analysis process from the current one to two months to about two weeks, reducing unnecessary activities in the bidding stage. In particular, the program enables the collection and analysis of accurate and consistent data, which is expected to enhance the reliability and efficiency of LCC analysis.
Among the components of LCC, the LAP focuses on maintenance costs. It can estimate and analyze both corrective and preventive maintenance costs.
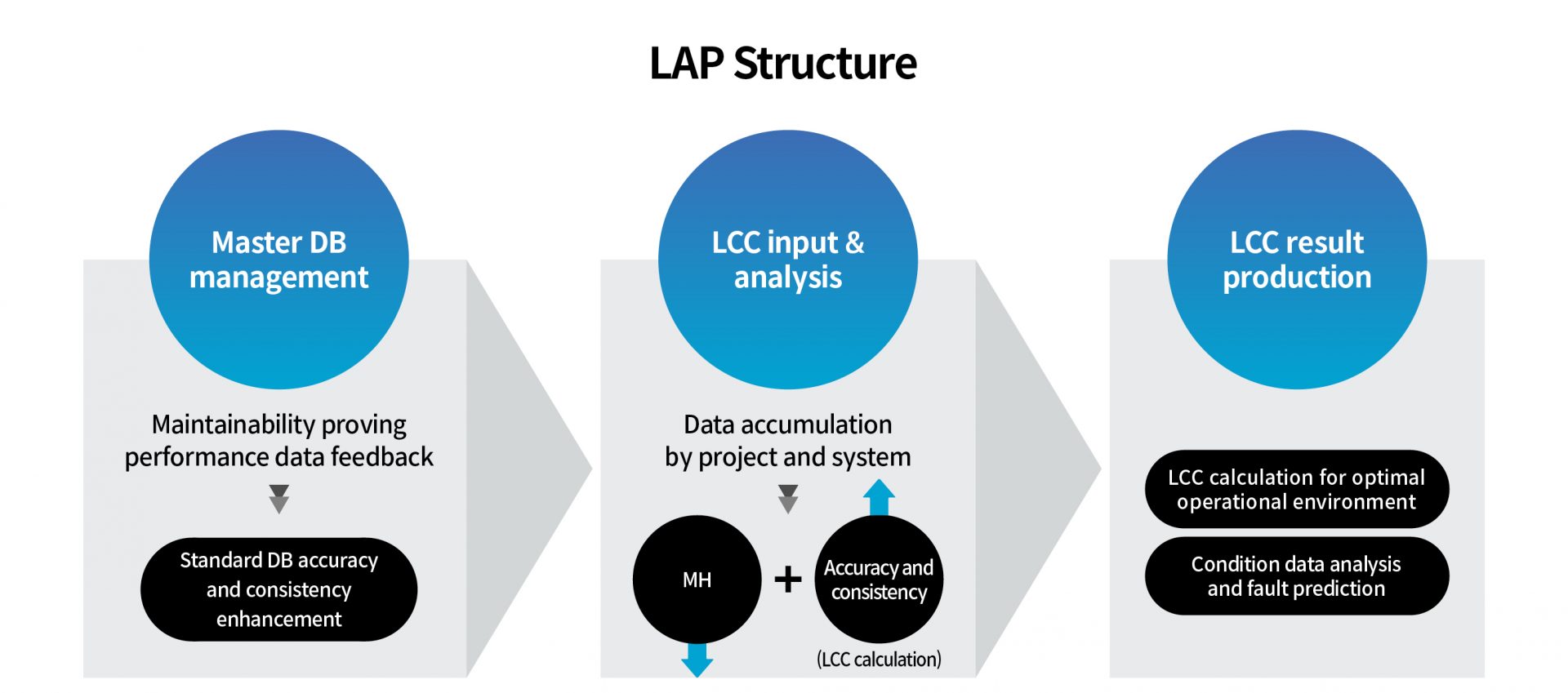
The LAP program for train maintenance cost analysis has three phases.
‘Master DB Management’ function manages data required for LCC analysis([4]PBS, [1]PM, [2]CM) This function allows the registration and management of preventive and corrective maintenance data on train parts and components requiring maintenance and subject to LCC analysis.
‘LCC Input and Analysis’ function accumulates and analyzes input and output data for LCC analysis by project and system. This function allows the registration and analysis of consumable and spare part costs and [3]MH for each maintenance activity.
‘LCC Result Production’ function calculates optimal LCC according to a repair scenario that meets project requirements, examines the results, and subsequently reanalyzes them by making adjustments to the specifics of [1]PM(maintenance intervals, maintenance hours) and [2]CM(fault rate, replacement, repair activities), which affect the LCC analysis the most, according to the requirements. The resulting outputs include LCC analysis by [4]PBS and [5]CBS, LCC analysis for consumables, LCC analysis by year, and analysis of labor costs.
[1] PM: Preventive Maintenance
[2] CM: Corrective Maintenance
[3] MH: Man Hour
[4] PBS: Product Breakdown Structure
[5] CBS: Cost Breakdown Structure
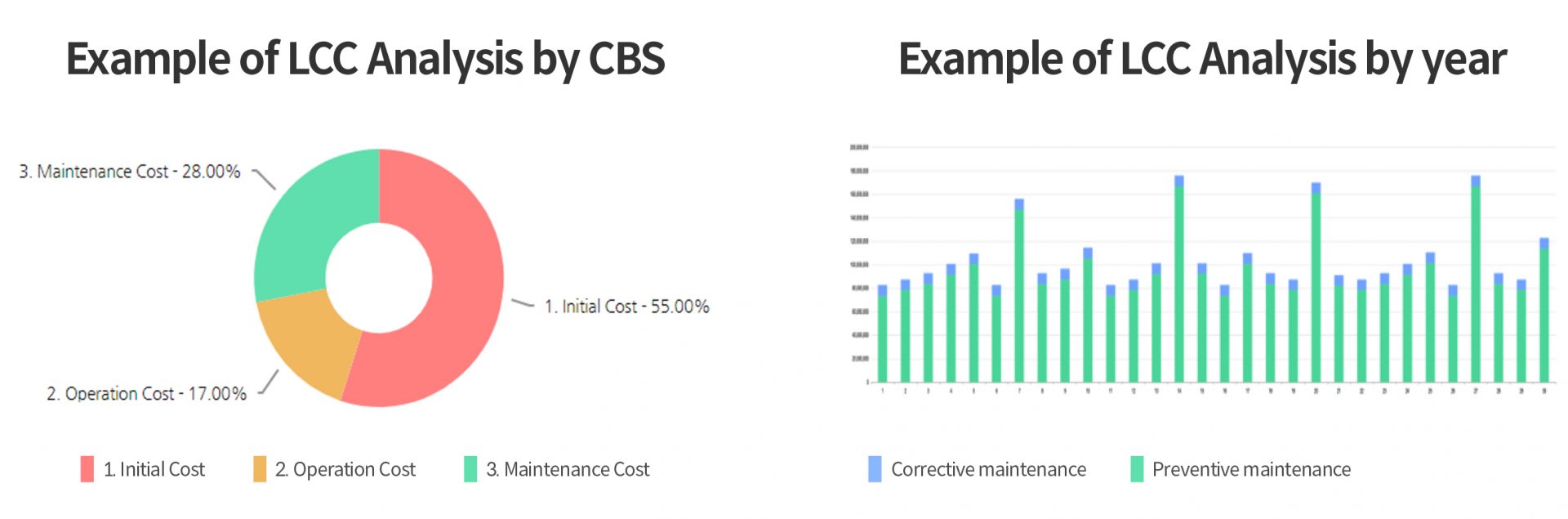

In the three processes, data plays a pivotal role as a fundamental element. To ensure the effective utilization of LAP, Hyundai Rotem is creating a master database to collect and utilize massive data accumulated from various projects to date, categorized by car, part manufacturer, and specification. The company also plans to continue collecting data and validating the accuracy and consistency in parallel to enhance the reliability of the program.
Moreover, for more systematic data accumulation and management, the company plans to divide it into six systems: running devices, brakes, electronic units, interiors, electricity, and communication. For each of these systems, a dedicated design manager will be assigned, responsible for conducting horizontal expansion while continuing data accumulation.
The implementation of LAP is expected to bring a greater synergy with Hyundai Rotem’s extensive expertise across various aspects of the train industry from design to manufacture, production, maintenance and operation. In the past, LCC calculations heavily relied on theoretical data extracted from papers and data books related to parts provided by part suppliers. However, with the LAP, it is now possible to gather real-world data obtained from actual maintenance sites and produce highly accurate and consistent calculations using the data.

The LAP is undergoing final testing such as security checks and error correction before it can be used in projects in the fourth quarter of 2023. Once the program is introduced, interested parties will be able to use it to enter data and produce LCC calculations. The company plans to continue collecting data from various car projects and expand the range of data applications, enhancing the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of the program to make it a highly useful tool.
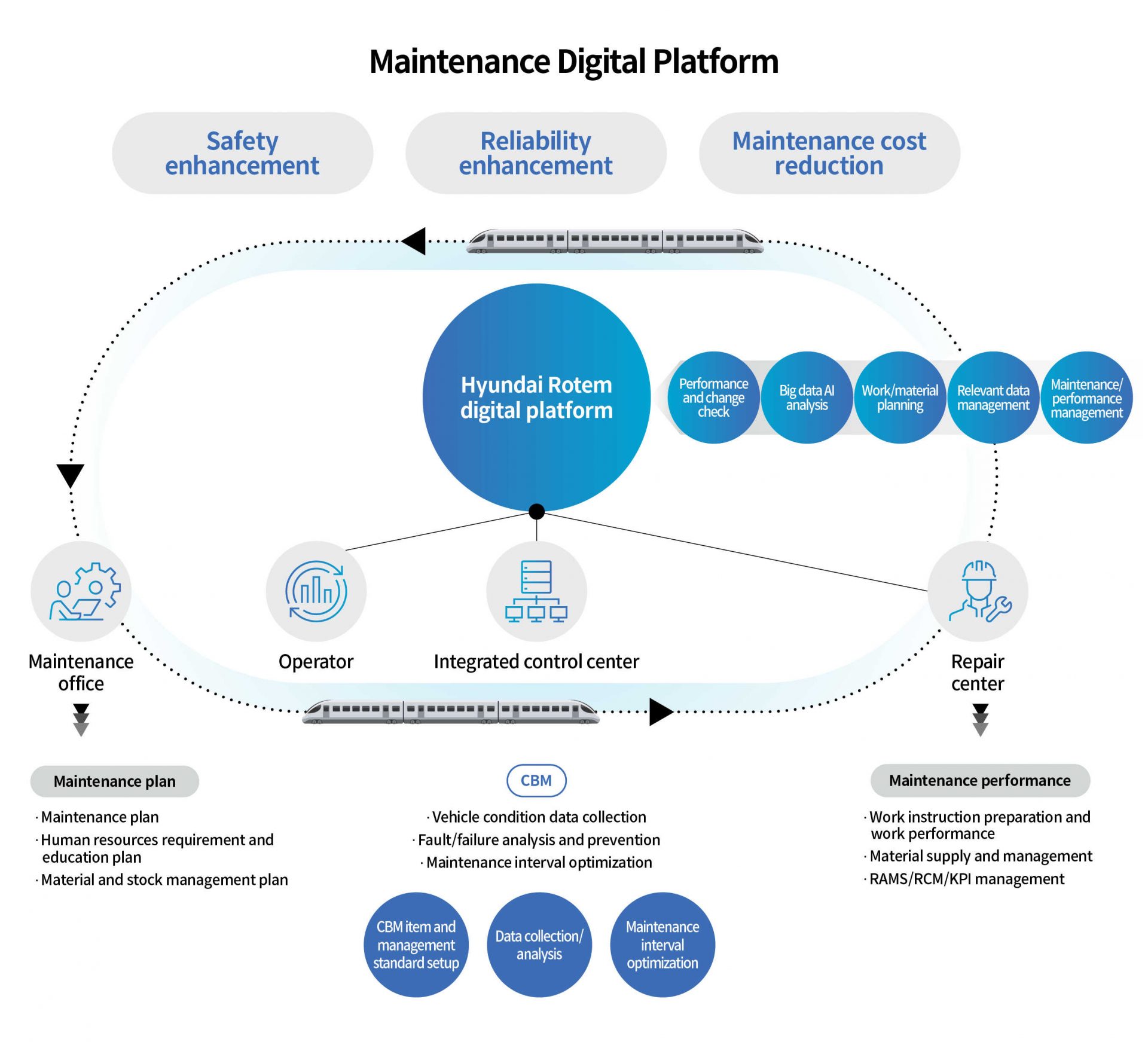
Furthermore, the program will be upgraded to connect with a maintenance digital platform starting in 2024. The upgrade may include the functions that synchronize and analyze based on a bill of materials (BOM), which is a critical element in train manufacturing, and the functions that correct exchange and inflation rates from existing data sources.
Hyundai Rotem LAP can improve the accuracy and consistency of LCC calculations and minimize maintenance costs, boosting competitiveness in the maintenance business that has recently launched. Additionally, it can reduce the time required for engineering review during LCC analysis, further enhancing competitiveness in bidding. Moreover, it can be connected with [1]FMECA and [2]FRACAS activities, as well as condition-based maintenance (CBM) systems, which is expected to enhance car safety and availability.
[1]FMECA : Failure Modes Effects and Criticality Analysis
[2]FRACAS : Failure Reporting, Analysis, And Corrective Action System



